Overview
In today’s fast-paced and competitive business landscape, making smart decisions is no longer just an advantage—it’s a necessity. Data has become the cornerstone of effective decision-making, offering actionable insights that empower businesses to stay ahead of the curve. Yet, leveraging data effectively requires more than access to information; it demands the ability to analyze, interpret, and implement insights strategically.
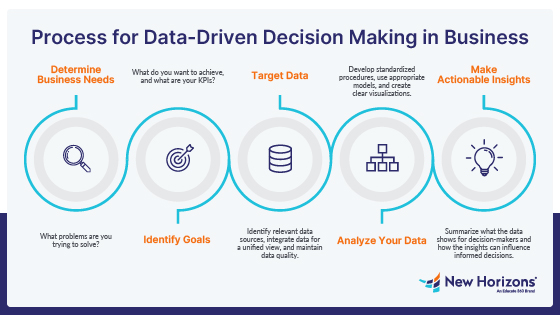
Source : Horizon (Data Driven Decision Making)
In this article, we’ll explore how data can be harnessed to make smarter business decisions, the tools and methodologies that drive this process, and practical examples of how data-driven strategies can transform businesses.
The Importance of Data-Driven Decision Making
Data-driven decision-making (DDDM) refers to the practice of basing strategic and operational choices on data analysis rather than intuition, guesswork, or past experiences alone. This approach offers several key advantages:
- Increased Accuracy: Data eliminates guesswork, allowing businesses to base their decisions on measurable and verifiable insights.
- Predictive Insights: Analyzing trends and patterns helps businesses anticipate future outcomes, enabling proactive rather than reactive strategies.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined operations and better resource allocation become possible when decisions are backed by solid data.
- Improved Customer Understanding: Data helps businesses gain deeper insights into customer behavior, preferences, and needs, fostering stronger relationships and loyalty.
Key Steps to Using Data Effectively
1. Identify Business Goals
Before diving into data collection and analysis, it’s crucial to define what you want to achieve. Are you looking to increase revenue, improve customer retention, or optimize operational efficiency? Clear objectives guide the type of data you collect and the metrics you prioritize.
2. Collect Relevant Data
Data comes in various forms—structured (e.g., financial figures, sales records) and unstructured (e.g., customer reviews, social media posts). Businesses should leverage multiple sources, including:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
- Website analytics
- Social media platforms
- Market research reports
- Internet of Things (IoT) devices
3. Ensure Data Quality
Poor-quality data leads to poor decisions. Implement data cleaning processes to eliminate inaccuracies, duplicates, and inconsistencies. Reliable data is timely, accurate, and relevant.
4. Leverage the Right Tools
Invest in analytics tools and software tailored to your needs. Options include:
- Business Intelligence Tools: Tableau, Power BI
- Data Analytics Platforms: Google Analytics, Apache Spark, Metabase
- Customer Analytics Tools: Mixpanel, HubSpot
5. Analyze and Interpret Data
Understanding data requires more than numbers—it demands context. Use techniques such as:
- Descriptive analytics to summarize past performance.
- Predictive analytics to forecast future trends.
- Prescriptive analytics to recommend actions based on insights.
6. Turn Insights Into Action
Data alone doesn’t drive results; the actions taken based on insights do. Translate findings into concrete strategies, whether that means tweaking a marketing campaign, reallocating resources, or launching a new product.
7. Monitor and Iterate
The business landscape is constantly evolving. Regularly monitor the impact of your decisions and adjust strategies as needed to remain aligned with objectives.
Practical Applications of Data in Business Decision-Making
1. Marketing Optimization
Data enables marketers to segment their audience, track campaign performance, and optimize spending. For example, analyzing customer demographics and behaviors can help craft targeted campaigns that yield higher ROI.
2. Supply Chain Management
Supply chains generate vast amounts of data, from inventory levels to delivery times. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify bottlenecks, predict demand, and reduce costs.
3. Financial Forecasting
Using historical financial data, businesses can create accurate forecasts, manage risks, and make informed investment decisions. Predictive models also help anticipate cash flow challenges.
4. Customer Experience Enhancement
Customer feedback, purchase histories, and interaction data can be used to personalize experiences. For instance, Amazon’s recommendation engine uses past purchase data to suggest products, boosting sales and customer satisfaction.
5. Human Resources and Workforce Planning
HR teams can use data to identify hiring trends, employee performance metrics, and attrition risks. Predictive analytics can forecast workforce needs, helping businesses plan effectively.
Challenges in Data-Driven Decision Making
While the benefits of using data are immense, businesses often face challenges, such as:
- Data Overload: Too much data can be as problematic as too little, leading to analysis paralysis. Prioritizing key metrics is essential.
- Data Privacy and Security: Compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA is critical to avoid legal repercussions and maintain trust.
- Skill Gaps: Data analysis requires expertise. Many businesses struggle to find or train employees with the necessary skills.
- Resistance to Change: Shifting from intuition-based to data-driven decision-making can encounter resistance within teams or leadership.
Case Study: Data-Driven Success
Company X faced declining sales and customer churn. By analyzing customer feedback, they discovered dissatisfaction with their mobile app’s usability. The company invested in redesigning the app based on data-driven insights, resulting in:
- A 30% increase in app engagement.
- A 20% reduction in churn.
- A 15% boost in sales within six months.
This example illustrates how actionable data insights can drive meaningful business improvements.
The Future of Data in Decision-Making
The rise of advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is taking data-driven decision-making to new heights. These technologies can process vast datasets in real-time, uncover hidden patterns, and provide predictive recommendations at a scale previously unimaginable.
As the Internet of Things (IoT) and 5G networks expand, the volume and variety of data available to businesses will continue to grow. Companies that adapt to these advancements and invest in robust data strategies will maintain a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Using data to make smarter business decisions isn’t just a strategy—it’s a mindset. It requires a commitment to continuous learning, investment in the right tools and talent, and a willingness to adapt to new insights. Businesses that embrace data-driven decision-making will not only navigate challenges more effectively but also unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation.
By turning data into actionable insights, you can transform your business into a more agile, customer-focused, and profitable enterprise. The question isn’t whether to use data—but how well you can use it to shape your future.